Oncology clinical trials represent a significant investment in the health industry. The costs of such trials can vary widely based on factors such as the number of patients, the type of intervention, and the location of the trial. Gene therapy and cell therapy are much more expensive than traditional interventions such as chemotherapy.
Moore et al wrote in JAMA Internal Medicine in 2020 that the median cost of a clinical trial between 2015 and 2016 was $19 million, but costs can easily range up to 100 times that.[4] For oncology trials, an average per-patient cost was reported to be $59,500 in a report by the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA).
As drug development costs continue to rise, the ability to predict and manage them becomes increasingly vital. To that end, the use of machine learning in estimating oncology trial costs has proven to be a valuable tool. One such tool is the Clinical Trial Risk Tool developed by Fast Data Science.
Fast Data Science’s Clinical Trial Risk Tool uses machine learning models to analyse clinical trial protocols, predict the cost of a trial, and identify the possible risks. The prices of each intervention in the protocol, including gene and cell therapy are considered, as well as the number of interventions all play a part in this prediction process. The tool successfully predicts the cost on a per-patient basis.
Above: the Clinical Trial Risk Tool lets you upload a protocol and will generate a site budget from the protocol and charge masters for you.
It is very difficult to obtain reliable cost data for clinical trials, since this is highly commercially sensitive data. However, some data is in the public domain due to public funding bodies, or freedom of information requests. In addition, a number of academic groups have published aggregate data. For a fee, it is possible to obtain commercial databases of trial costs, but these are very expensive.
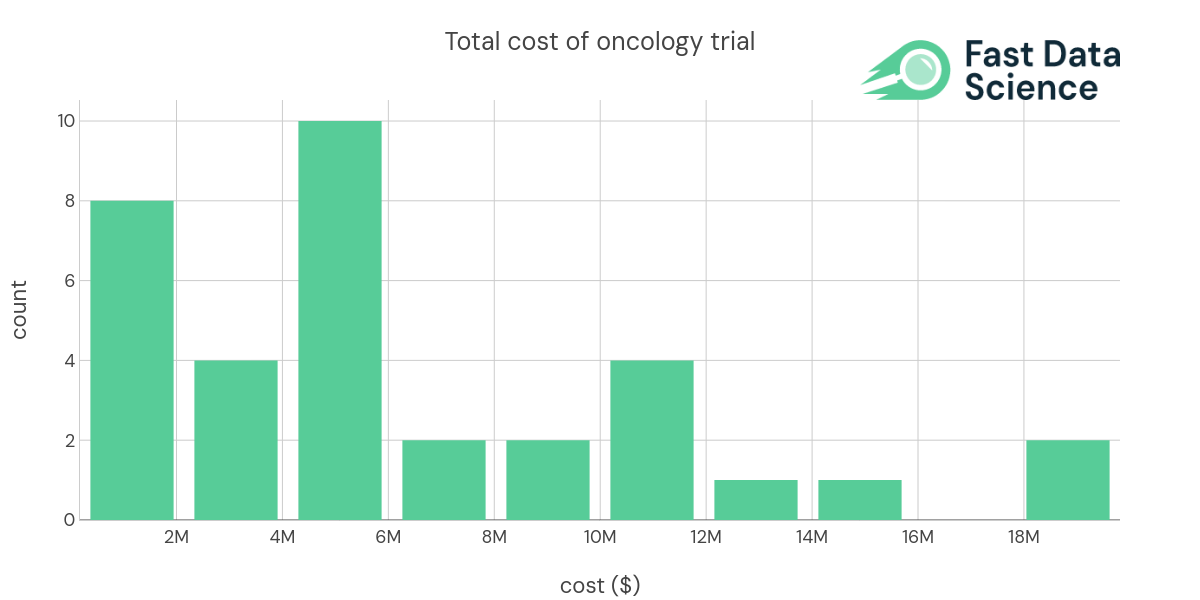
We are including below a subset of an oncology cost dataset. Some of this data is available publicly on the Grants Dashboard of the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
| indication (longer) | Technology | CT.gov URL | Enrollment | Trial Phase | Total Cost | Per Patient Cost ($PP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Myeloid Malignancy | biologic drug | 30 | Phase 1 | 328000 | 10933.3 | |
| Blood Cancer | biologic drug | NCT03483324 | 9 | Phase 1 | 5000000 | 555556 |
| Blood Cancer | biologic drug | NCT03925935 | 24 | Phase 1 | 6192579 | 258024 |
| B cell cancers, Leukemia | biologic drug | NCT03088878 | 156 | Phase 1/2 | 18292674 | 117261 |
| Blood Cancer | biologic drug | NCT02222688 | 26 | Phase 1 | 4179598 | 160754 |
| Colon Cancer | biologic drug | NCT02953782 | 112 | Phase 1/2 | 10234048 | 91375.4 |
| Leukemia, Acute Myeloid (AML) | biologic drug | NCT03248479 | 96 | Phase 1 | 5000000 | 52083.3 |
| Blood Cancer, Solid Tumors | biologic drug | NCT02216409 | 88 | Phase 1 | 6505568 | 73926.9 |
| Breast Cancer | biologic drug | NCT00781612 | 720 | Phase 3 | - | 104186 |
| Stage IV Melanoma | cell therapy | NCT00438984 | 11 | Phase 1 | 936164 | 85105.8 |
| Stage IV Breast Cancer | cell therapy | NCT00791037 | 23 | Phase 1/2 | 2236359 | 97233 |
| Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | cell therapy | NCT00850785 | 6 | Phase 1 | 653850 | 108975 |
| Brain Cancer | cell therapy | NCT02546102 | 414 | Phase 3 | 5391016 | 13021.8 |
| Leukemia, Acute Myeloid (AML) | cell therapy | NCT03301597 | 146 | Phase 2 | 4310000 | 29520.5 |
| Melanoma | cell therapy | NCT01875653 | 4 | Phase 3 | 3000000 | 750000 |
| Blood Cancer, Bone Marrow Transplant and Viral Infection | cell therapy | NCT03475212 | 60 | Phase 1/2 | 4825587 | 80426.4 |
| Brain Cancer | cell therapy | NCT02208362 | 92 | Phase 1 | 12753854 | 138629 |
| Brain Cancer, Breast Cancer | cell therapy | NCT03696030 | 39 | Phase 1 | 9015149 | 231158 |
| Multiple Myeloma | cell therapy | NCT03288493 | 180 | Phase 1 | 19813407 | 110074 |
| B cell cancers, Leukemia | cell therapy | NCT03233854 | 57 | Phase 1 | 11034982 | 193596 |
| Lung Cancer | cell therapy | NCT03546361 | 36 | Phase 1 | 11815315 | 328203 |
| Melanoma, Skin cancer | cell therapy | NCT03240861 | 12 | Phase 1 | 14144221 | 1.17869e+06 |
| Sarcoma | cell therapy | NCT03240861 | 12 | Phase 1 | 4693839 | 391153 |
| HIV-related Lymphoma, HIV/AIDS | gene therapy | NCT02797470 | 18 | Phase 1/2 | 8414265 | 467459 |
| Prostate cancer | small molecule drug | 232 | Phase 2/3 | 2969523 | 12799.7 | |
| Acute Myeloid Leukemia | small molecule drug | 60 | Phase 1/2 | 1166746 | 19445.8 | |
| Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | small molecule drug | 140 | Phase 2 | 5852288 | 41802.1 | |
| Solid Tumors | small molecule drug | NCT01954316 | 48 | Phase 1 | 5683693 | 118410 |
The Clinical Trial Risk Tool is a valuable resource for the health industry, as it helps to identify and quantify the potential risks associated with a specific trial and maneuver through the budgeting process more confidently. Moreover, it helps with both Phase 1 and Phase 2 oncology trial duration and cost estimation.
One of the big advantages of using machine learning in oncology trial cost prediction is it provides a means to analyse complex and multifaceted data, and learn patterns or trends, much faster than humans. Our oncology clinical trial software can significantly reduce the time it takes to estimate the cost of clinical trials.
Cost your oncology protocol
The costs associated with clinical trials are immense, but with the aid of advanced technology and machine learning, researchers can get an accurate estimate of a trial’s cost from the protocol. Despite the inherent difficulties in predicting such complex costs, tools like Fast Data Science’s Clinical Trial Risk Tool provide a promising option to navigate this challenging landscape.
In 2016, Sertkaya et al used aggregate data from Medidata solutions to calculate average trial costs by phase and therapeutic area.[6] Sertkaya et al reported that oncology trials cost an average of $4.5 million in Phase 1, $11.2 million in Phase 2, and $22.1 million in Phase 3. Should you use these figures, we advise to take care to update them according to inflation and consumer price index as they are now out of date.
In 2025, Mulcahy et al used SEC filings to estimate trial costs, and modelled costs on the basis of patient months rather than individual trials.[5] They calculated mean R&D costs of $1.31 billion with standard deviation $1.92 billion for all phases of a drug’s development. The fact that the standard deviation is greater than the mean shows the inherent difficulty we face in modelling trial costs. Mulcahy et al did not report any major change to the average development cost when oncology trials were included from their dataset.